Embryology .
It is so interesting how we are all made.

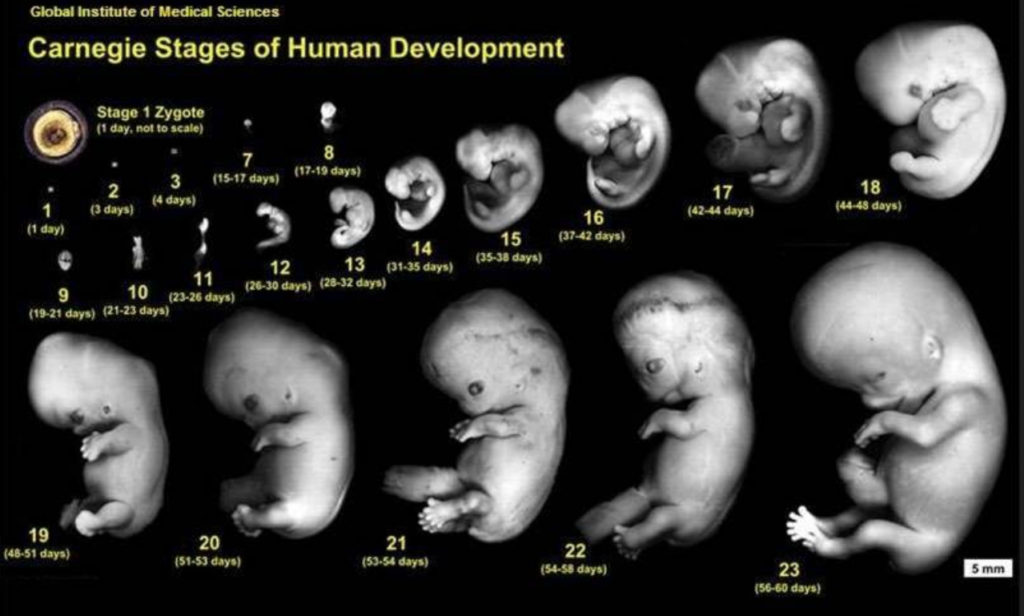
The amazing changes that take place to make a baby.
1st Week: The fertilized egg (zygote), undergoes mitotic cell division, becoming a solid ball of cells (morula), which enters the uterus by the 4th day. It develops into the first single layer of cells (blastula), with fluid filling it centrally to form a blastocoele. Then the inner cell mass forms (embryoblast) , while the outer cell layer (trophoblast) continues to grow , at this stage it is called a “blastocyst/ blastocyte”. Then upon implantation in the uterine wall (day 7), the most amazing thing happens- cells of the inner cell mass move and rearrange (gastrulation) (a.k.a. morphogenetic movements) to form the primary germ layers (gastrula): epiblasts= primitive ectoderm, hypoblasts=primitive endoderm, continuing into 2nd week.
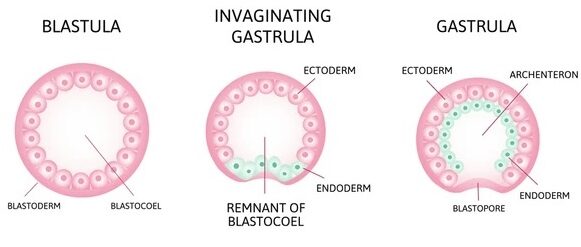
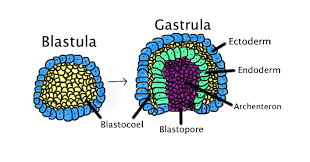
The archenteron (primary gut/ digestive tube of the developing conceptus) feeds and develops the endoderm and mesoderm.
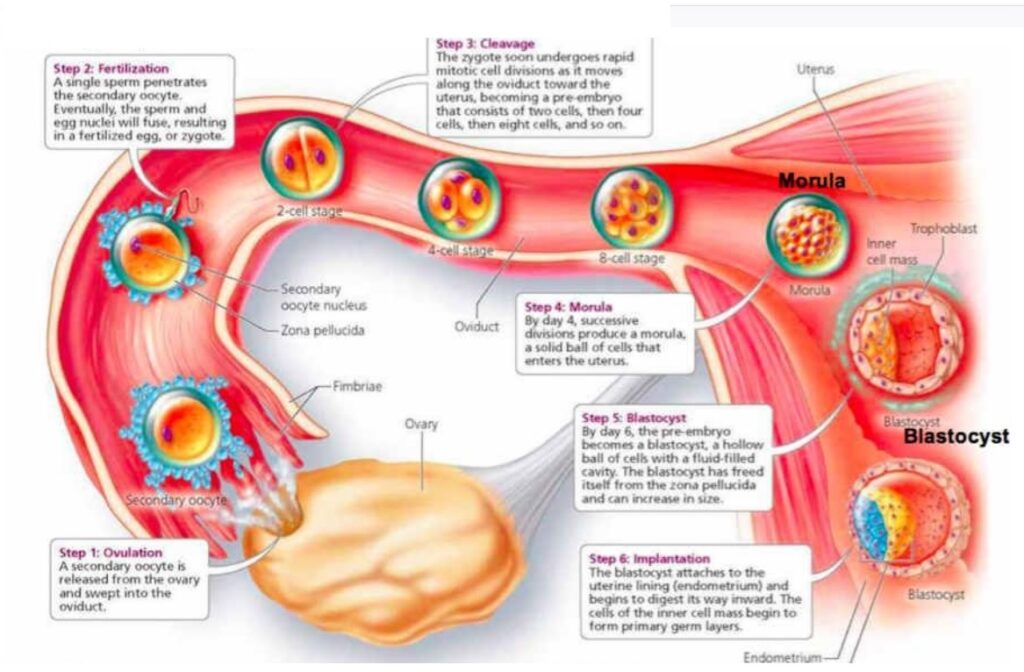
2nd Week: A Primitive placenta begins to form. The trophoblast forms (a major part of) the placenta, as the blastocyst deepens its hold in the uterine wall. Day 9: inner cell mass differentiates into two cell types, forming the bi-laminar embryonic disc by Day 12: epiblast (which also forms the amniotic sac) & hypoblast (which also form the yolk sac).
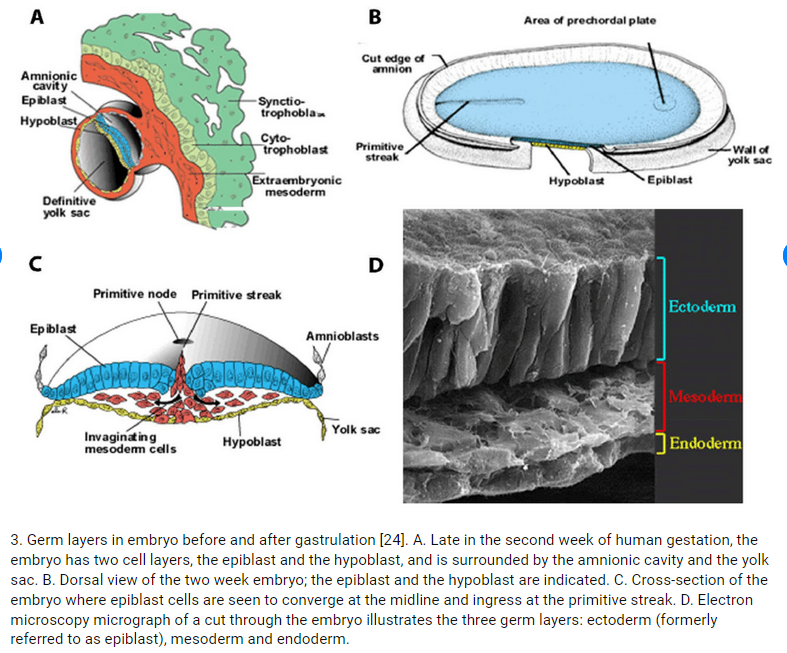
3rd Week: The primitive umbilical cord begins to form. Day 15-16:The blastocyte further develops into the 3 discs. Epiblast (ectoderm) cells that enter the primitive streak node/ pit are converted by EMT -Epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and enter to fill the mesoderm and endoderm layers. Two days later (by day 18) the middle mesoderm layer will grow and spread to cover around the entire other two connected layers.
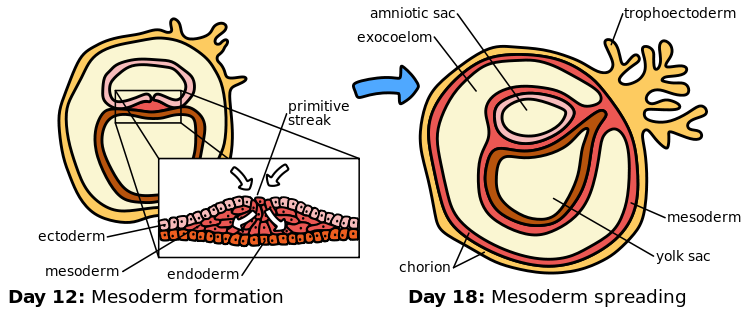
 EACH DISC GIVES RISE TO DEVELOPMENT OF CERTAIN STRUCTURES:-
EACH DISC GIVES RISE TO DEVELOPMENT OF CERTAIN STRUCTURES:-
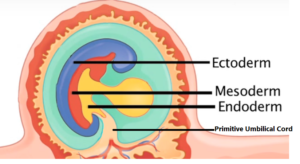
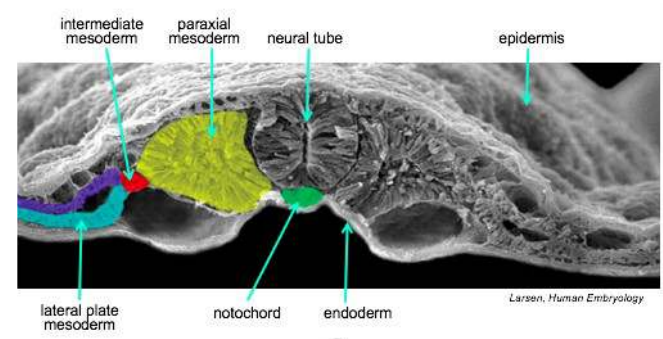
ENDODERM: Primitive Gut: intestinal tube, Mucous membranes, Thyroid/Glands, Lung bud lining, Urinary bladder & ureters, Yolk sac
MESODERM: Heart, Vascular system, Blood cells, Dermis, Subcutaneous, Connective tissues, Muscles, Skeleton, Genitals, Lymphatics, kidneys,
ECTODERM: Epidermis, Hair, Sebaceous & Sweat glands, Nervous System
“Vitelline circulation is the system of blood flowing from the embryo to the yolk sac and back again. The yolk-sac is situated on the ventral (front) aspect of the embryo; it is lined by endoderm, outside of which is a layer of mesoderm. It is filled with fluid ( vitelline fluid) , which is utilized for the nourishment of the embryo during the earlier stages of its existence. Blood is conveyed to the wall of the sac by the vitelline arteries (a branch of the dorsal aorta), and after circulating through a wide-meshed capillary plexus, is returned by the vitelline veins to the tubular heart of the embryo. This constitutes the vitelline circulation, and by means of it nutritive material is absorbed from the yolk-sac and conveyed to the embryo.” (Ref.Inorporating 20th edition of Gray’s Anatomy )
HEART EMBRYOLOGY
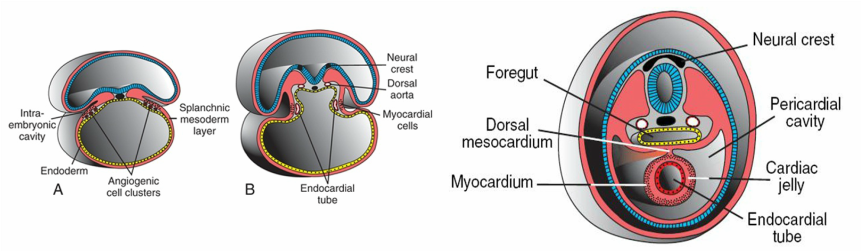
Cardiogenesis: The cardiogenic region is a horseshoe shaped group of cells. The heart starts out as two separate tubes, by day 19, and as the embryo undergoes lateral folding, the two tubes combine into one “Single Cardiac Tube”, merging together, still leaving the ends unmerged either side (two at one end , and two at the other end). The single combined tube section starts to swell and begins to beat by end of the 3rd week- day 22(this is too early/ too small to see on ultrasound).
By day 23, the heart begins to bend and fold: “atrioventriculobulbar loop”
Dextral Looping: The cardiac tube will twist a& turn on itself in a RIGHTWARD direction – normal development.
Levo Looping: The cardiac tube twists on itself in a LEFTWARD direction- abnormally reversing the ventricles right to left, & left to right.
By Day 28: Folding of the embryonic disc has occurred in both longitudinal (cephalocaudal) and transverse (lateral) planes.
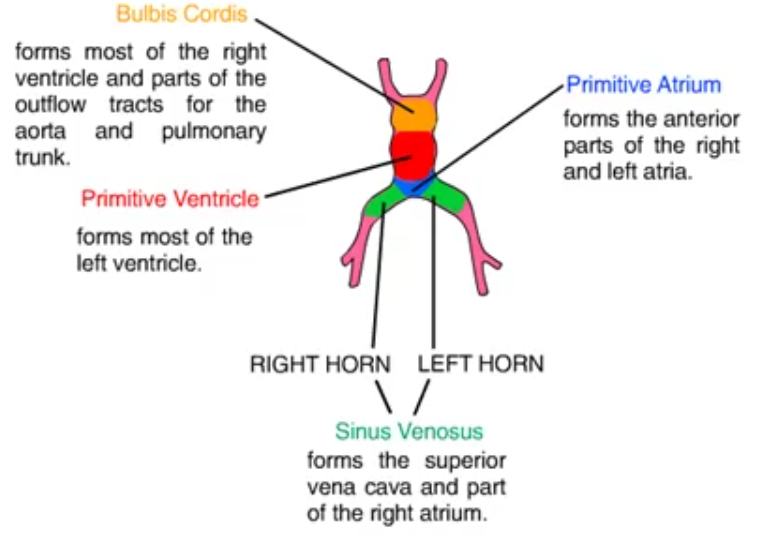
4th Week: The Atrial & Ventricular Septums begin to form, arising as layers : Septum Primum, Septum Secundum (side by side act as an opening interatrial valve – foramen ovale in fetal life), and Endocardial Cushion tissue. The Endocardial Cushion tissue is in the middle of the heart, from which arises the tricuspid & mitral valves, part of Atrial septum and part of the ventricular septum.
Secundum ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) = when S.Primum layer does not reach secundum to close the flow in later life. Primum ASD is an opening in the lower atrial septum from problems in the endocardial cushion, and commonly involves the mitral and/or tricuspid valves.
Embryology key terms•Embryonic disc•Cardiogenic mesoderm•AV and sinus nodes•Primitive heart tube•Bulbus cordis•Aortic arch•Truncus arteriosus•Septum primum•Septum secondum•Endocardial cushion
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gastrulation
https://anat550.sitehost.iu.edu/cvanim/htube/htube.mov
EMBRYOLOGY of IVC
The incredible changes that take place to construct the main draining vessel of the body called the IVC. Weeks 6 -8 (Just 3wks).
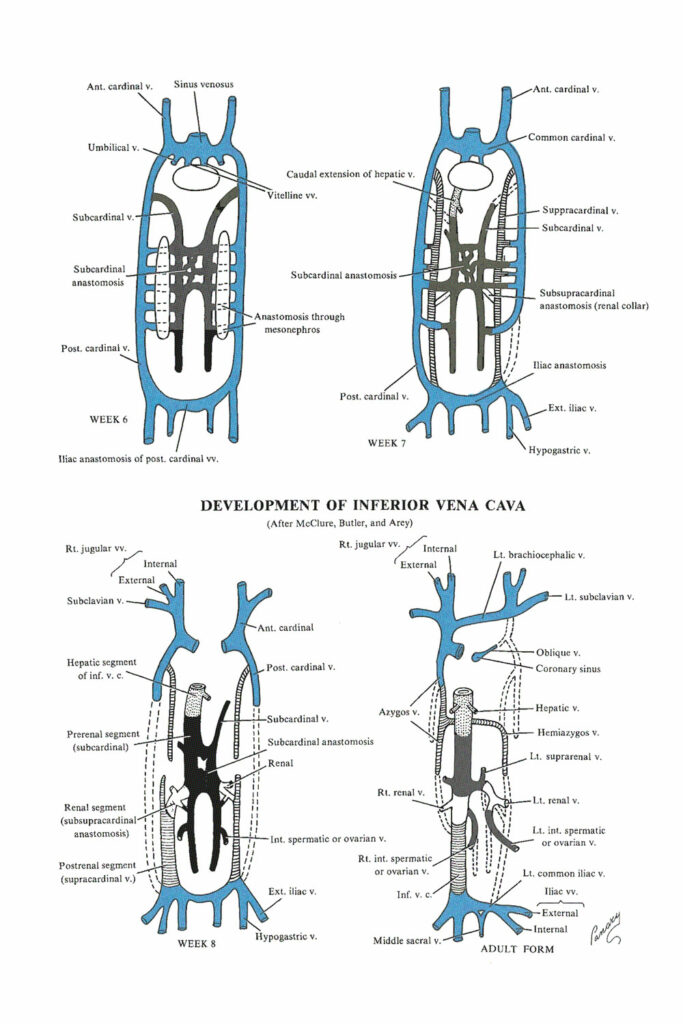
- IN SUMMARY: the definitive inferior vena cava is composed of (from caudal to cranial)
- The posterior intercardinal anastomosis
- The caudal portion of the right supracardinal vein
- The right anastomosis between the supracardinal and the subcardinal veins
- A segment of the right subcardinal vein
- The anastomosis between the right subcardinal and right vitelline veins
- The terminal portion of the right vitelline vein
Reference: https://discovery.lifemapsc.com/library/review-of-medical-embryology/chapter-126-development-of-the-venous-system-the-inferior-vena-cava
KIDNEY Embryology
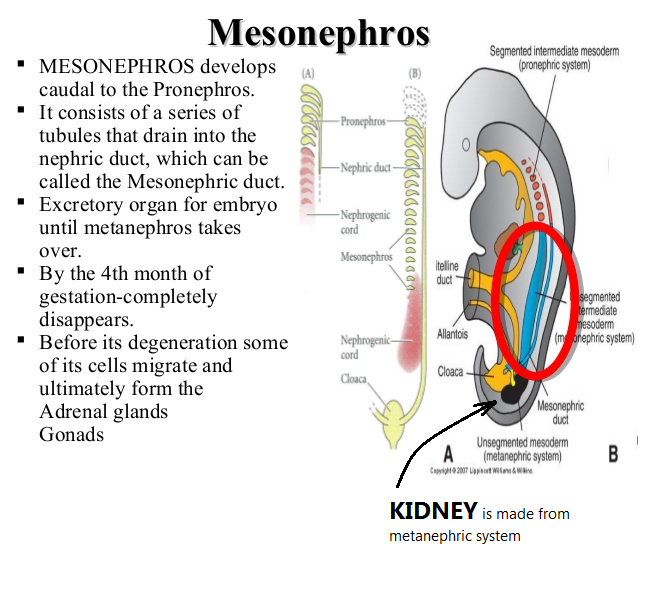

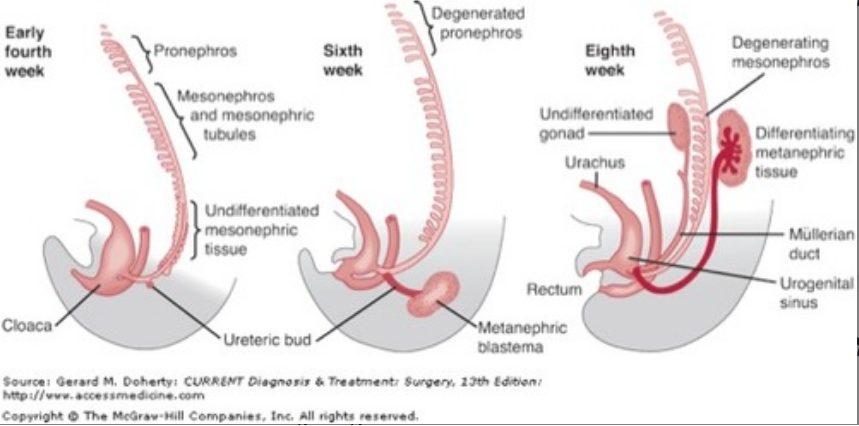
The kidney moves up, while the gonads have to move down.
https://quizlet.com/gb/509246738/embryology-urogenital-development-flash-cards/